Hass Avocado Tree
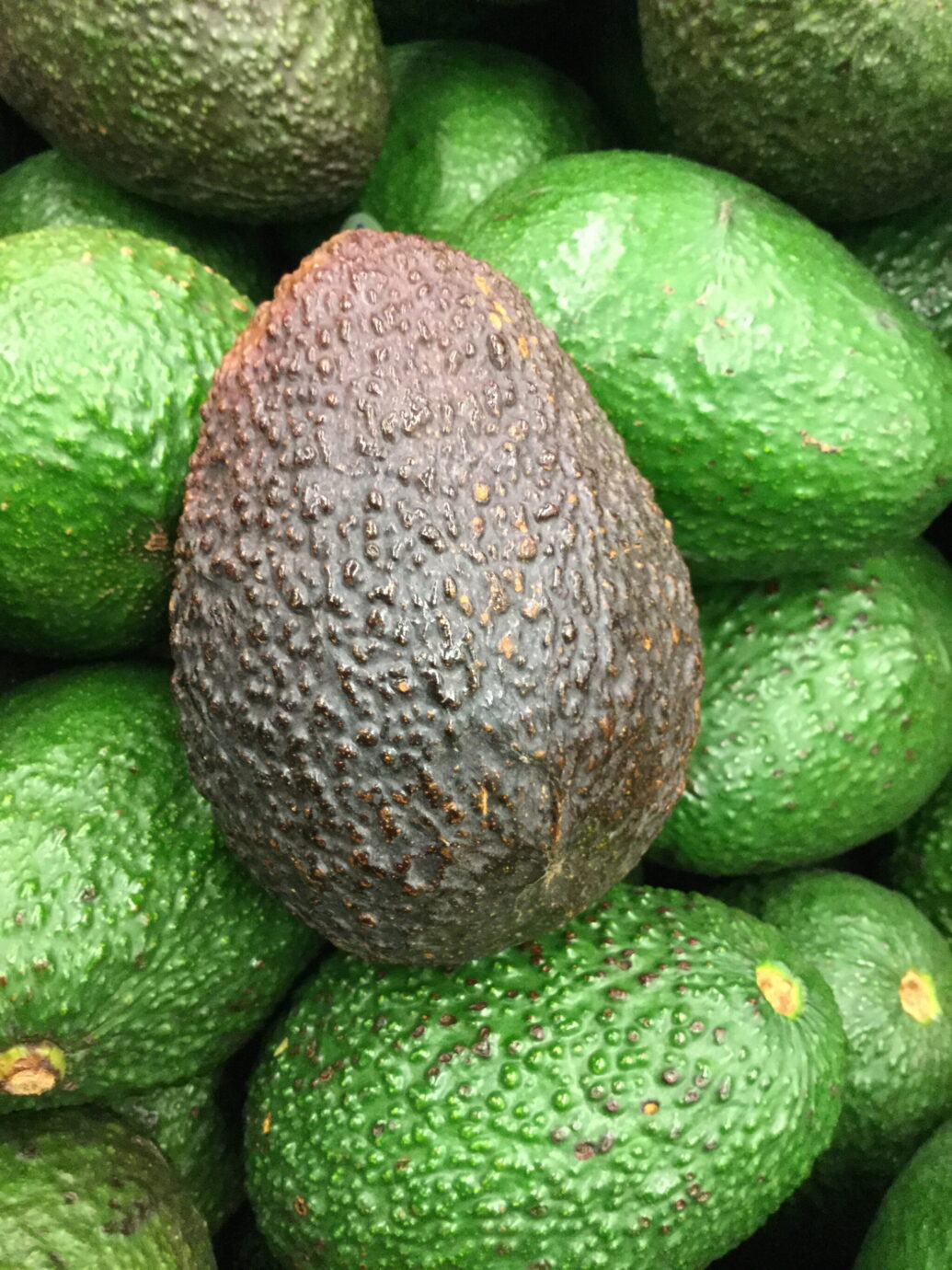
The Hass Avocado is the #1 most popular Avocado in California because it is self-fruitful and has a long fruiting season. The fruit has dark green-colored, bumpy skin which becomes a dark purplish-black when ripe. It is a Type A Avocado that can pollinate Type B Avocados. Avocado trees need morning sun and afternoon shade and can not handle overly windy areas. At younger ages, they only fruit once every other year.
Not compatible with your zone (2a)
General Plant Information
Hass Avocado Tree Information and Care
Hass avocado tree is the most commercially popular avocado tree in the world. It was first grown by a Southern California amateur horticulturist Rudolph Hass who named it. The fruit is great tasting, good size and shelf-life, and high yields in some areas. 95% of the California Avocado crop!
In the San Fernando Valley California, young Hass avocado trees’ leaves are often damaged when planting in areas with too much afternoon sun during the hot dry summers. This is due to the large surface area of the avocado tree and dry climate in the valley. Planting them in areas with afternoon shade will protect the tree from excessive sunlight that causes yellowing and browning of the leaves.
Near freezing temperatures that can occur during Winter nights can also damage the Hass Avocado tree, causing leaves to blacken and dry. Hass Avocado trees do well by the coast in areas such as Malibu, Ventura, Santa Barbara, and San Diego where the ocean regulates the temperature.
Hass Avocados have dark green-colored, bumpy skin which becomes a dark purplish-black when ripe. It was first grown by a Southern California amateur horticulturist Rudolph Hass who named it. Hass Avocados are great tasting, have a good size and shelf-life, and high yields in some areas. 95% of the California Avocado crop!
In Los Angeles and the San Fernando Valley California, young Hass Avocado tree leaves can be damaged by the full Summer sun. Therefore, plant where they will receive morning sun and afternoon shade to protect from sun damage. Protect from cold winds in the Winter because near freezing temperatures that occur during Winter nights can also damage the Hass Avocado tree. As a result, this will cause leaves to blacken and dry. The Hass Avocado does great by coastal areas such as Malibu, Ventura, Santa Barbara, and San Diego where the ocean regulates the temperature.
Hass Avocado trees are also grown in areas such as Glendale, Burbank, Pasadena, Sherman Oaks, Encino, Tarzana, Reseda, Woodland Hills, West Hills, Calabasas, Agoura, Thousand Oaks, but their microclimate should be considered.
Botanical Info
Medium to large tropical evergreen with large green to dark green leaves, and white flowers grouped in inflorescences. The same flower will open as both female and male at different times of the day depending on if Type A or Type B cultivar. Avocados can self-pollinate depending on temperature, but most plant Type A (Hass) and Type B (Fuerte) to ensure cross-pollination.
Avocado trees can become alternate bearing, producing a large crop one-year small crop next year. Mature fruit is dull when hanging on the tree, and ripen once picked.
Planting
If planting in a location with high winds, plant near a windbreak. To avoid sunburn on fruit, plant where the tree will receive morning sun and afternoon shade. Ideally, plant in well-drained soils with moderate temperatures. Newly planted trees need to be irrigated on average twice a week to establish a strong root system.
Maintenance
Pruning can be done in Winter to maintain the shape and size of the tree. Trim so that the skirt of the tree does not touch the ground. Irrigate and maintain moist soil making sure to keep tree trunk dry. Fertilize with nitrogen throughout the year in small doses. Keep area atop roots well mulched, ideally with natural leaf litter and/or organic chunky mulch.
Additional Information
Watering : RegularSun Exposure : Full Sun near the Coast or in mild summer climate. Plant in afternoon shade in areas with hot summer climates.
Plant Type: Evergreen
USDA Hardiness Zones: 8-11
Pollination: Self Pollinating - but more productive with pollinator
Chill Hours: Less 100 hours below 45°F
Planting Information
Soil and Planting: Plant in soil that drains well. Dig a hole that is as deep as the tree’s roots and at least twice as wide.
Place the tree in the hole and backfill around the plant’s roots with a mixture of the native soil and high-quality planting mix that has washed sand and organic fertilizer.
Create a basin around the roots drip zone so that water collects. Water deeply until the roots and nearby soil is saturated and reaches field capacity.
Plant Care Information
Limited Guarantee and Returns
Compatibility
The two factors that determine if a deciduous fruit trees will grow well and produce fruit in a certain area are the Chill Hour Requirement and the Cold Hardiness. “Chill hours” are the amount of cold a deciduous fruit tree need to produce fruit. This is measured in the number of hours below 45 degrees Fahrenheit a plant must experience during its winter dormancy. Paradise Nursery only grows Low Chill fruit trees that meet the chill requirements of all areas of the United States.
The second factor is Cold Hardiness. Cold Hardiness refers to the minimum temperature a plant can tolerate. The USDA’s Cold Hardiness Zones indicate the average minimum winter temperatures of areas. Based on the shipping zipcode, our website will only allow you to add plants to your cart that grow within your USDA Hardiness Zone, and tolerate your climate.
Pollination & Propagation
(Grafting/Cutting) Most of Paradise Nursery’s edible plants are self-fruitful. Self-pollinating trees do not require an additional tree to produce fruit. For your convenience, we have indicated which trees require a pollinator, and their associated pollinators. Only the sweet cherries, avocados, and some plums require a pollinator. All of our other propagated edible plants do not require a pollinator. All of our edible plants are either grown from cuttings, budded, or grafted. This way, we can ensure that our plants are high quality and fruit immediately. Plants will generally begin fruiting within a year of planting.